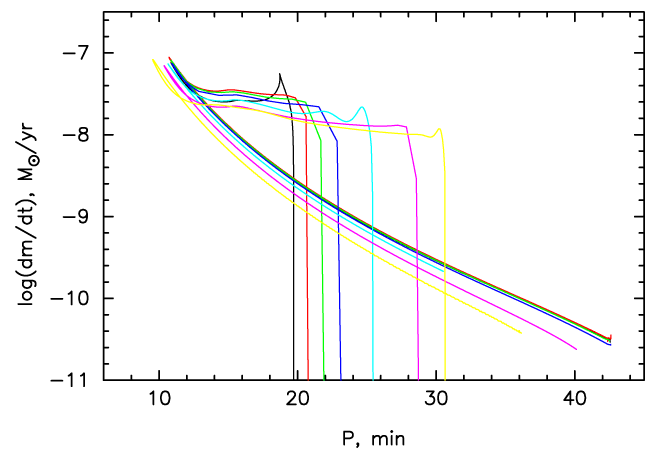
Figure 25: Mass-loss rate vs. orbital period dependence for semidetached systems with He-star
donors and WD accretors, having post-common envelope 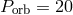 to 130 min. Initial masses of
components are
to 130 min. Initial masses of
components are 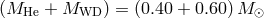 . He abundance in the cores of the donors at
RLOF ranges from 0.98 to 0.066 (left to right). Image from [870], copyright by the author.
. He abundance in the cores of the donors at
RLOF ranges from 0.98 to 0.066 (left to right). Image from [870], copyright by the author.
 to 130 min. Initial masses of
components are
to 130 min. Initial masses of
components are 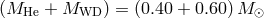 . He abundance in the cores of the donors at
RLOF ranges from 0.98 to 0.066 (left to right). Image from [870], copyright by the author.
. He abundance in the cores of the donors at
RLOF ranges from 0.98 to 0.066 (left to right). Image from [870], copyright by the author.
