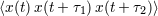 ; it gives the
contribution to the third moment from the product of three Fourier components having frequencies which add to zero. It has
been used in many fields, notably geophysics, to study weak nonlinearities (see, e.g., [56, 80]).
; it gives the
contribution to the third moment from the product of three Fourier components having frequencies which add to zero. It has
been used in many fields, notably geophysics, to study weak nonlinearities (see, e.g., [56, 80]).- Articles
- Journal
- Home
sidebar
"Low-Frequency Gravitational Wave Searches
Using Spacecraft Doppler Tracking"
Using Spacecraft Doppler Tracking"
J. W. Armstrong
The bispectrum is the Fourier transform of the third-order lagged product 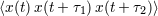 ; it gives the
contribution to the third moment from the product of three Fourier components having frequencies which add to zero. It has
been used in many fields, notably geophysics, to study weak nonlinearities (see, e.g., [56, 80]).
; it gives the
contribution to the third moment from the product of three Fourier components having frequencies which add to zero. It has
been used in many fields, notably geophysics, to study weak nonlinearities (see, e.g., [56, 80]).
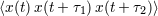 ; it gives the
contribution to the third moment from the product of three Fourier components having frequencies which add to zero. It has
been used in many fields, notably geophysics, to study weak nonlinearities (see, e.g., [56, 80]).
; it gives the
contribution to the third moment from the product of three Fourier components having frequencies which add to zero. It has
been used in many fields, notably geophysics, to study weak nonlinearities (see, e.g., [56, 80]).